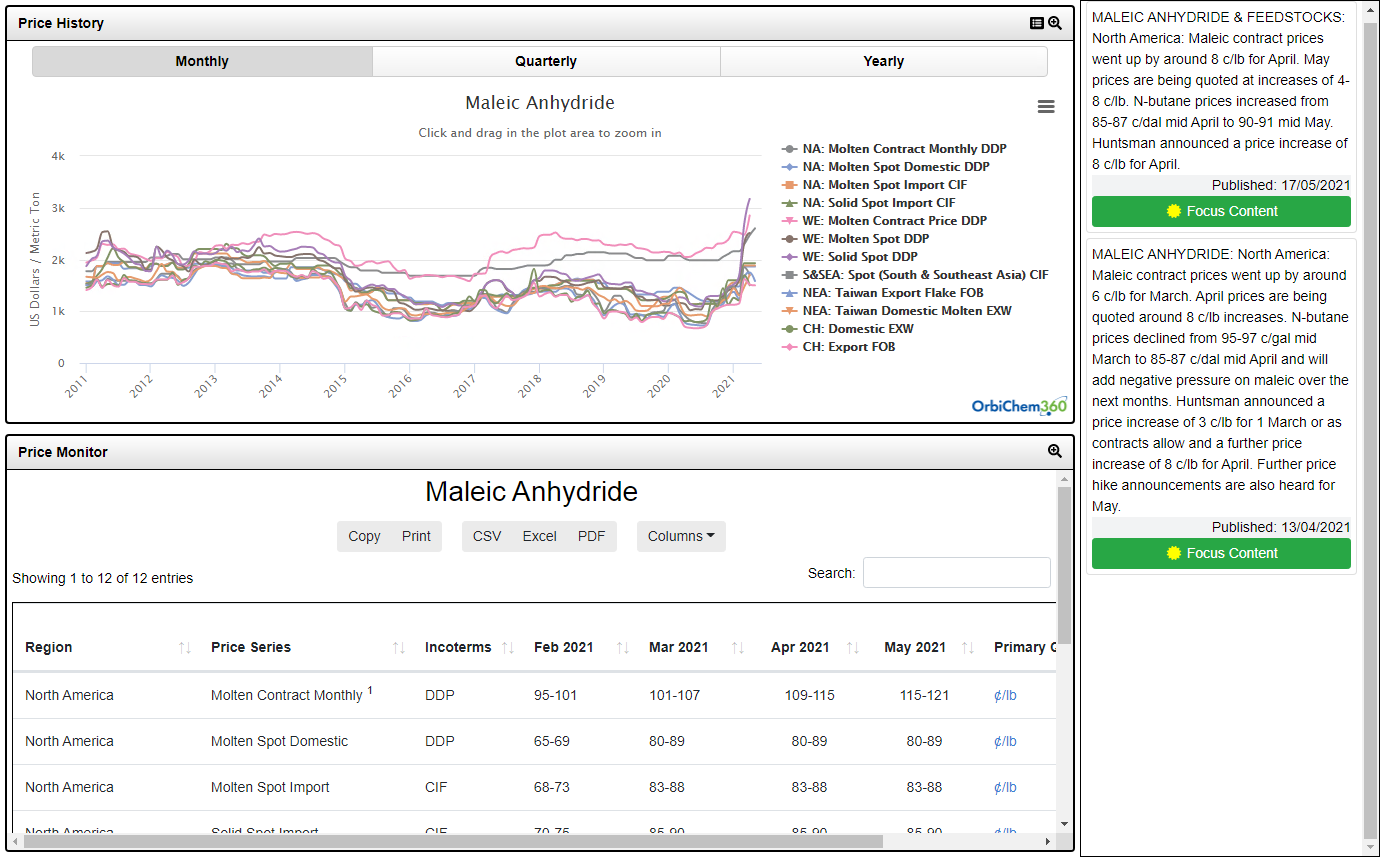
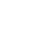
A chemical intermediate, maleic anhydride can be produced from three feedstocks – benzene, butane and phthalic anhydride waste. Maleic anhydride markets are very regionalized, although there is some inter-regional trade. More than 50% of maleic anhydride is used to produce unsaturated polyester resins (UPR). Applications for UPR include boat hulls, car parts, furniture and pipes. Maleic anhydride is also used in the production of plasticisers and dibasic acids such as fumaric acid, maleic acid and succinic acid.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Propylene oxide (PO) is a chemical intermediate produced from propylene. Traditionally two methods involving hydrochlorination and the other involving oxidation were employed. PO can be produced with styrene monomer as a coproduct (POSM process). More recently, a new process known as HPPO in which propylene is oxidized with hydrogen peroxide was introduced commercially. The main end use is in the manufacture of polyether polyols which are used in conjunction with isocyanates to produce polyurethanes. The second major use is in the production of propylene glycols. Other uses include the production of glycol ethers and ,in some cases, butanediol.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
1,4 Butanediol, commonly known as BDO, is a chemical intermediate that was originally obtained though reaction of acetylene with formaldehyde, known as the Reppe process. Other popular technologies use butane/maleic anhydride, propylene oxide and butadiene as feedstocks. In recent years bio-based BDO production technology has been developed as an alternative to the traditional raw materials. BDO is used in polyurethane production via tetrahydrofuran (THF) which is used to make polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG) which is used in spandex production. Its other major downstream market is polybutadiene terephthalate (PBT), a thermoplastic polyester used in the production of engineering materials.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Unsaturated polyester resins (UPR) production is based on phthalic anhydride, isophthalic acid, maleic anhydride, styrene monomer and glycols. Polyester resins represent around 10% of styrene and over half of maleic anhydride consumption, globally. Applications include the construction and marine sectors, as well as pipes and tanks.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Benzene is consumed primarily in the production of ethylbenzene and styrene monomer, cumene and phenol, cyclohexane, chlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, alkylbenzene and maleic anhydride as well as a chemical intermediate. Benzene can be sourced from reformate, pyrolisis gasoline, toluene disproportionation and the hydrodealkalation of toluene.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) is an engineering thermoplastic used in applications including automotive, electrical and electronic components, appliances and household items such as toothbrush fibres. It is a polyester and is made by the reaction of 1,4-butanediol with either PTA (purified terephthalic acid) or DMT (dimethyl terephthalate). It has good electrical properties and is heat resistant up to 150oC, or 200oC when reinforced with glass fibre. It offers lower water absorption than polyamide and better chemical and environmental stress crack resistance than polycarbonate.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid currently produced either from conversion of petroleum-derived maleic anhydride or from bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates. Historically, the high cost of producing succinic acid from petroleum feedstock limited its use to a narrow range of applications such as pharmaceuticals and food ingredients. The growing availability of biobased succinic acid is opening applications such as plasticizers, polyurethanes, personal care products, deicing solutions, resins and coatings, lubricants, and as a building block for a number of chemical intermediates. Succinic acid can be used to produce 1,4 butanediol (BDO), tetrahydrofuran (THF) and polybutylene succinate (PBS) biodegradable resins.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Polyester polyols are produced by the condensation of a glycol and a dicarboxylic acid or acid derivative. The three general types of polyester polyols are manufactured from aliphatic diacids, aromatic diacids or caprolactone. Raw materials include phthalic anhydride and adipic acid. The functionality, structure and molecular weight of the polyester polyol differ depending on the type of polyurethane application. In some applications, polyester polyols compete with polyether polyols. Uses include rigid foam for use in the construction/insulation market and performance coatings, elastomers and flexible foams.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG) is used primarily for elastomer production, with spandex fibres being the key end use. Other end uses include polyurethane resins used in the production of synthetic leather, flexible adhesives and coatings and solid elastomers. PTMEG is commonly produced through acid catalyzed polymerization of THF which is derived from 1,4 butanediol. It is available in various molecular weights and offers hydrolytic stability and a high degree of flexibility.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Spandex, also known as elastane, is a segmented polyurethane. The major raw materials used in the manufacturing process are PTMEG and pure MDI. Spandex can be produced through dry, wet or melt spinning, with dry spinning being the most common method. Due to it exceptional elasticity, spandex can be stretched significantly without breaking and still retains its original shape. Its major applications are in clothing, underwear and sportswear where comfort and elasticity are paramount. When used for clothing spandex fibres are often mixed with cotton, polyester etc with the amount of spandex determining the elasticity.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Natural gas is a hydrocarbon gas consisting mainly of methane produced from decomposing vegetation and animal matter. Natural gas is a non-renewable, fossil fuel used for heating, cooking and electricity. It is also used as a fuel and as a chemical feedstock.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Butadiene is the third of the major olefins, after ethylene and propylene. It is extracted from C4 streams, mainly from steam crackers but also from refinery cat crackers. It has been called ‘the co-product of a co- product’ but is really an important chemical in its own right. Its major outlets include production of the engineering plastic ABS (acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene) and the synthetic rubber SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber), a major constituent of vehicle tyres. The volumes of butadiene produced are largely influenced by the operating rates of ethylene crackers and the feedstock used.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects


 ChemFocus
ChemFocus ChemFacts
ChemFacts ChemForesight
ChemForesight ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules)
ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules) Consulting
Consulting