- Expertise
- CHEMICAL PORTFOLIO
- Acetic Acid • Vinyl Acetate
- Acrylic Acid & Acrylate Esters
- Chlor-Alkali & Derivatives
- Epoxy Resins & Co-Reactants
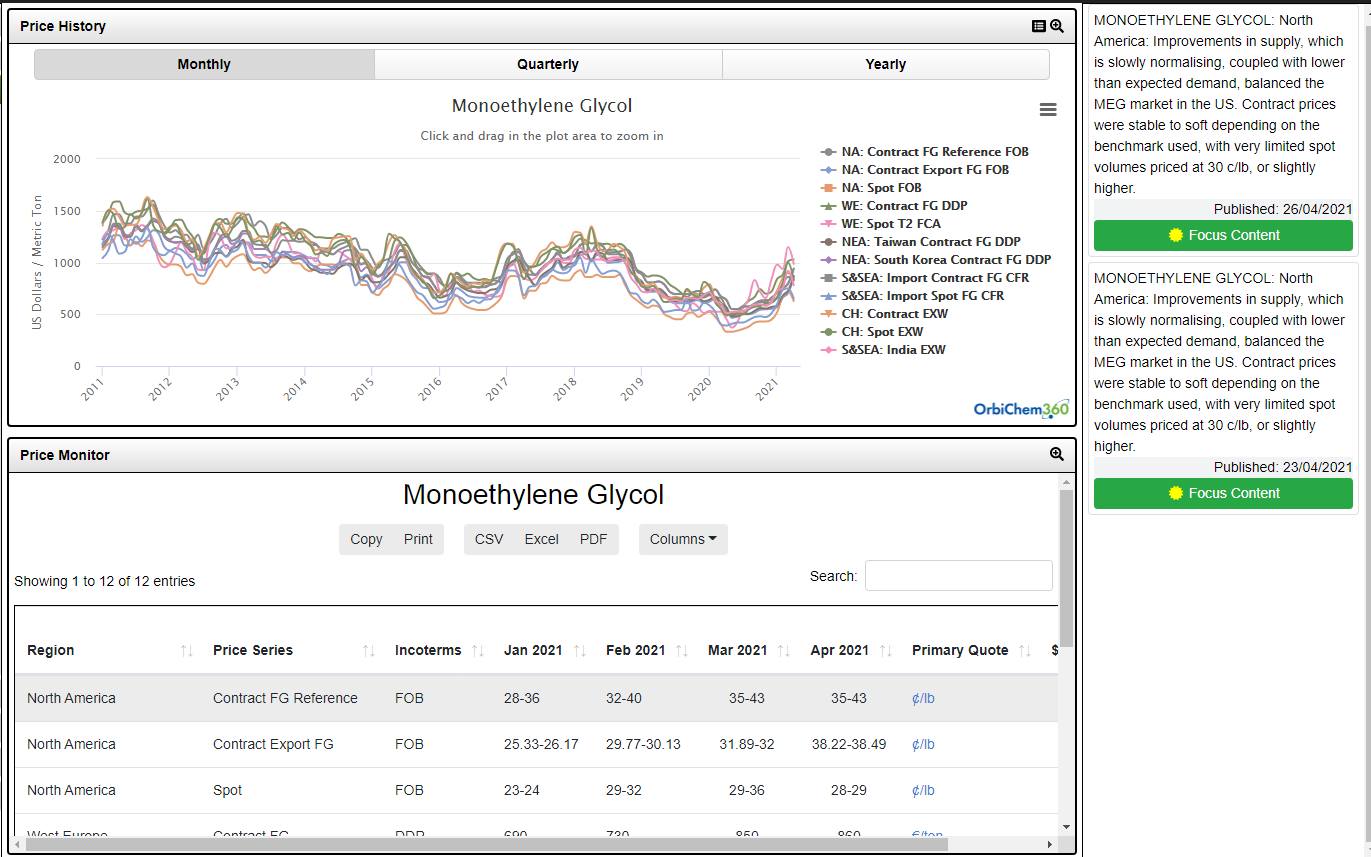
- Ethylene Glycols • EO & EODS
- Fibres & Intermediates
- Maleic Anhydride • 1,4-Butanediol & Derivatives
- Orthoxylene • Phthalic Anhydride
- Phenol • Acetone & Derivatives
- Plasticisers • Oxo Alcohols
- Polyester & Intermediates
- Polyurethanes & Intermediates
- Unsaturated Polyester Resin
- Aromatics
- Olefins
- RESOURCES
- COMPANY
INDUSTRIES
OrbiChem360
OrbiChem360 provides comprehensive chemical business intelligence to assist business managers in their strategic planning and business performance optimisation.
MARKET DATA, INSIGHTS & INTELLIGENCE
CONSULTING SERVICES
Specialist and Strategic Advisory Services
OrbiChem360
OrbiChem360 provides comprehensive chemical business intelligence to assist business managers in their strategic planning and business performance optimisation.
Main Menu
- MAIN MENU
- Expertise
- Chemical Portfolio
- Acetic Acid • Vinyl Acetate
- Acrylic Acid & Acrylate Esters
- Chlor Alkali & Derivatives
- Epoxy Resins & Co-Reactants
- Ethylene Glycols • EO & EODS
- Fibres & Intermediates
- Maleic Anhydride • 1,4-Butanediol & Derivatives
- Orthoxylene • Phthalic Anhydride
- Phenol • Acetone & Derivatives
- Plasticisers • Oxo Alcohols
- Polyester & Intermediates
- Polyurethanes & Intermediates
- Unsaturated Polyester Resin
- Aromatics
- Olefins
- Resources
- Company
- LOGIN


 ChemFocus
ChemFocus ChemFacts
ChemFacts ChemForesight
ChemForesight ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules)
ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules) Consulting
Consulting