Benzene is consumed primarily in the production of ethylbenzene and styrene monomer, cumene and phenol, cyclohexane, chlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, alkylbenzene and maleic anhydride as well as a chemical intermediate. Benzene can be sourced from reformate, pyrolisis gasoline, toluene disproportionation and the hydrodealkalation of toluene.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Toluene is used primarily as an octane booster in gasoline. It is also used as a feedstock via disproportionation, in which benzene and xylenes are produced, and in hydrodealkylation (HDA) to make benzene, as well as in several chemical applications. Feedstock for benzene and xylenes is toluene's main chemical use. Other chemical applications include TDI and solvents. Toluene grades are: TDI-grade (over 99% purity); nitration (98.5%) for solvents and phenol and commercial (96%) for gasoline blending and as a feedstock for HDA and TDP. Most toluene is produced via catalytic reforming of naphtha in the process of gasoline manufacture.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Propylene is the second of the major olefins, after ethylene. It is co-produced together with ethylene in steam crackers and also by refinery cat-crackers and, increasingly, dehydrogenation of propane. Propylene has become much more than just a co-product. It is growing faster than ethylene and various processes for on-purpose propylene production have been developed to provide incremental capacity. Propylene's major derivative is polypropylene but it is also used to produce acrylonitrile, plasticiser alcohols and other chemicals.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
MDI or methylene diphenyl diisocyanate is an important raw material for polyurethanes. MDI undergoes a series of complex manufacturing stages. The process starts with benzene and nitric acid, and via aniline and formaldehyde reactions is also subsequently phosgenated to the final mix of isomers, which are distilled to the desired series of end-products. MDI is used in polyurethane chemistry by reaction with polyols, to produce a wide range of flexible and rigid foams, and elastomers, adhesives and coatings.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
TDI or toluene diisocyanate is a key raw material for polyurethane applications. The starting point for TDI is toluene and nitric acid, which thereafter undergo phosgenation reactions as well as distillation to arrive at the final range of TDI isomers. TDI is used in polyurethane chemistry by reaction with polyols, to produce a wide range of applications. TDI is produced in different grades, either for slab polyurethane foam which makes up the major end use sector, or for coatings adhesives sealants and elastomers applications. Flexible foam is largely used in mattress and furniture production.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
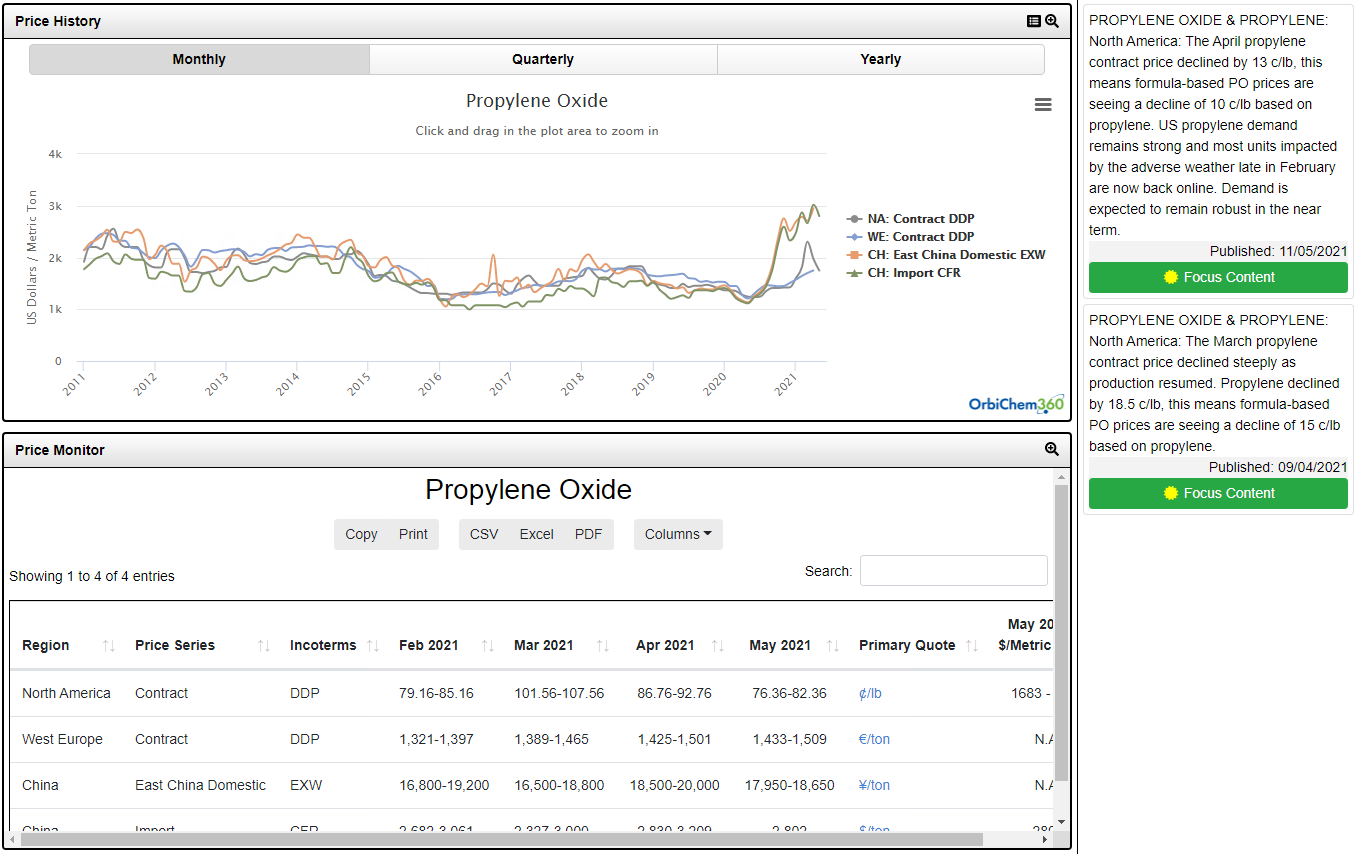
Propylene oxide (PO) is a chemical intermediate produced from propylene. Traditionally two methods involving hydrochlorination and the other involving oxidation were employed. PO can be produced with styrene monomer as a coproduct (POSM process). More recently, a new process known as HPPO in which propylene is oxidized with hydrogen peroxide was introduced commercially. The main end use is in the manufacture of polyether polyols which are used in conjunction with isocyanates to produce polyurethanes. The second major use is in the production of propylene glycols. Other uses include the production of glycol ethers and ,in some cases, butanediol.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Propylene glycol is a chemical intermediate obtained by hydration of propylene oxide. Di- and Tripropylene glycols, as well as small quantities of higher glycols, are also produced in the reaction. End markets are many and varied, one of the major uses being unsaturated polyester resins, which are used in surface coatings and glass fibre reinforced resins. Another very seasonal segment is in antifreeze and aircraft de-icing applications. USP grade MPG is used as a humectant in food and cosmetic applications, as a solvent for colouring and flavouring agents, and in various pharmaceutical uses.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
1,4 Butanediol, commonly known as BDO, is a chemical intermediate that was originally obtained though reaction of acetylene with formaldehyde, known as the Reppe process. Other popular technologies use butane/maleic anhydride, propylene oxide and butadiene as feedstocks. In recent years bio-based BDO production technology has been developed as an alternative to the traditional raw materials. BDO is used in polyurethane production via tetrahydrofuran (THF) which is used to make polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG) which is used in spandex production. Its other major downstream market is polybutadiene terephthalate (PBT), a thermoplastic polyester used in the production of engineering materials.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Adipic acid is a chemical intermediate used in the production of nylon 66 resin and nylon 66 fibre or in polyol and polyurethane production. By far the largest demand is in nylon 66 production for both fibre and resin, whilst the remainder is consumed in non-nylon applications including polyurethanes. It is produced by oxidising cyclohexane to cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone, generally with a catalyst, and then the products are reacted with nitric acid to form adipic acid.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Polyether polyols together with isocyanates are essential precursors in the manufacture of polyurethanes. Although the highly reactive isocyanate group is the unique feature of polyurethane technology, it is the polyols that in large part determine the properties of the final polyurethane polymer. Polyether polyols are hydroxyl-functional polymers usually made from the reaction of PO and or EO with an initiator. There are various kinds of polyols, but polyether polyols account for the lion’s share of the polyol market. Rigid polyols are reacted with MDI to make rigid foam, and flexible polyols are reacted with TDI to make flexible foam.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Polyester polyols are produced by the condensation of a glycol and a dicarboxylic acid or acid derivative. The three general types of polyester polyols are manufactured from aliphatic diacids, aromatic diacids or caprolactone. Raw materials include phthalic anhydride and adipic acid. The functionality, structure and molecular weight of the polyester polyol differ depending on the type of polyurethane application. In some applications, polyester polyols compete with polyether polyols. Uses include rigid foam for use in the construction/insulation market and performance coatings, elastomers and flexible foams.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG) is used primarily for elastomer production, with spandex fibres being the key end use. Other end uses include polyurethane resins used in the production of synthetic leather, flexible adhesives and coatings and solid elastomers. PTMEG is commonly produced through acid catalyzed polymerization of THF which is derived from 1,4 butanediol. It is available in various molecular weights and offers hydrolytic stability and a high degree of flexibility.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
PU Coating System consist of both dry and wet coatings. Dry coatings are made by spreading PU resin onto release papers. This is then dried and stuck onto various fabrics. After drying the pattern on the paper is transferred to the resin. There are two principle technologies for dry coating. Each method has specific characteristics. The major downstream use for these types of coating is polyurethane synthetic leather. Wet coatings are produced by adding DMF solvents and other additives to the basic resin. The material is then deaerated and dipped or coated to the base fabric. After further processing the resin is shaped into the finished product.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
PU sole resin is generally divided into three classifications according to hardness, density and use. Polyurethane based sole resin is very flexible in its usage and offers a wide range of properties according to the type of footwear. Sole resin also can be used in resin for inner sole and outer sole. Feedstocks include adipic acid, MDI and ethylene glycol.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects
Spandex, also known as elastane, is a segmented polyurethane. The major raw materials used in the manufacturing process are PTMEG and pure MDI. Spandex can be produced through dry, wet or melt spinning, with dry spinning being the most common method. Due to it exceptional elasticity, spandex can be stretched significantly without breaking and still retains its original shape. Its major applications are in clothing, underwear and sportswear where comfort and elasticity are paramount. When used for clothing spandex fibres are often mixed with cotton, polyester etc with the amount of spandex determining the elasticity.
-
 Market Analysis
Market Analysis
-
 Prices
Prices
-
 Trade Data
Trade Data
-
 Market Summary
Market Summary
-
 Price Forecasts
Price Forecasts
-
 Supply/Demand
Supply/Demand
-
 Single Client Projects
Single Client Projects


 ChemFocus
ChemFocus ChemFacts
ChemFacts ChemForesight
ChemForesight ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules)
ChemExpert (includes ChemFocus modules) Consulting
Consulting